The role of ACTH and glucocorticoid signaling in brown fat metabolism
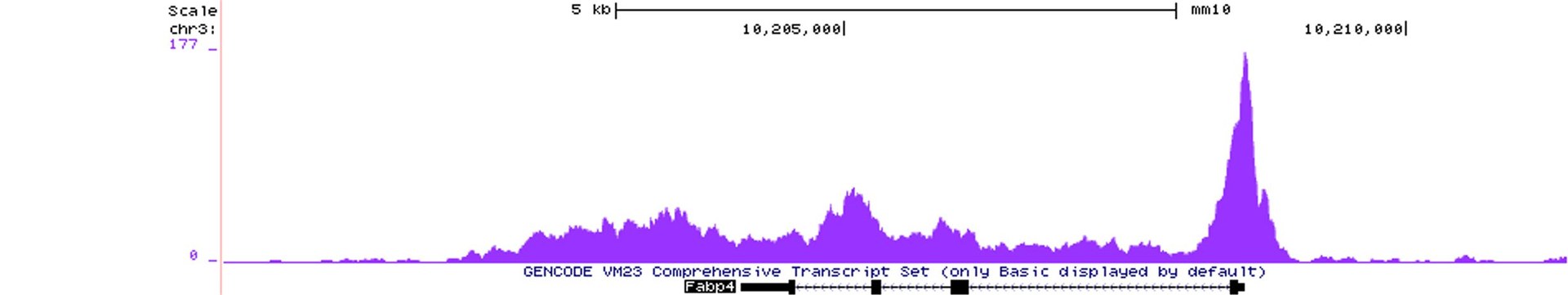
GR binding at the Fabp4 locus.jpg
© Prof. Henriette Uhlenhaut
Endocrine signals from the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis control metabolic pathways in many tissues, including brown fat. Indeed, ACTH stimulates, while glucocorticoids inhibit thermogenesis. Here we aim to dissect the physiological effects of the HPA axis on brown fat function. We will decipher the crosstalk between glucocorticoid, ACTH, lipid and cytokine signaling under various conditions such as feeding, cold and high fat diet challenges using mouse genetics, genomics, metabolomics and proteomics. We will determine the relevance of these pathways and their intersection in brown fat function and metabolic disease.
Project Leaders
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Nina Henriette Uhlenhaut
Chair for Metabolic Programming TUM School of Life Sciences Weihenstephan & ZIEL-Institute for Food & Health
Gregor-Mendel-Str. 2
85354 Freising
Director Institute for Diabetes and Endocrinology (IDE) Helmholtz Zentrum München
Ingolstaedter Landstr. 1
85764 Neuherberg
© TUM
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Yongguo Li
University Hospital, University of Bonn
Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology
Venusberg-Campus 1 53127 Bonn
© Li
